Digital Reference
Digital Reference (DR) - upper ontology introduced by the H2020/ECSEL project Productive4.0 in 2017, is a supply chain-related Semantic Web mirror of the semiconductor industry and supply chains containing semiconductors.
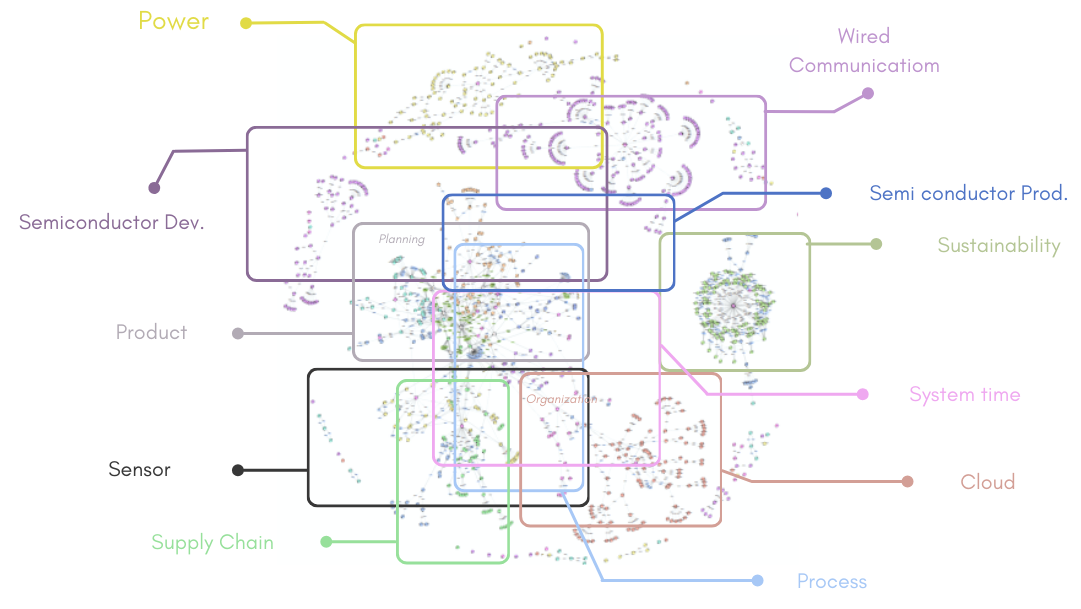
The Digital Reference, organized in topic clusters (lobes), provides the structure of a knowledge base readable for humans and computers alike. It represents all stages of the semiconductor supply chain with several sub-ontologies that currently consist of concepts, hierarchies and organizations (Ehm et al. 2019), (Ehm et al. 2020), (Ramzy et al. 2022).
Introduction
-
The concept of Digital Reference originates from the Productive4.0 initiative, aligned with the principles of Industry 4.0. Productive4.0 aimed to create a comprehensive user platform fostering digital networking across industries and value chains, inspired by the Semantic Web, Semantic Web Stack, and ontology.
-
At its core, this innovative approach is a Semantic Web model capturing intricate supply chain networks in the semiconductor industry and related domains. Merging distinct supply chain structures and semiconductor production concepts, it provides a holistic understanding of this complex landscape. This model includes around 800 distinct classes, representing various concepts across diverse domains. These are organized into thematic clusters known as "lobes," analogous to functional regions in the human brain. Each lobe corresponds to a specific supply chain facet, acting as a repository of knowledge accessible to both humans and machines. For instance, the "Cloud" lobe symbolizes networked remote servers for data management, the "Power" lobe covers electrical energy consumption, and the "Product" lobe encapsulates customer-tailored items and services. Additionally, lobes encompass domains like "Semiconductor Development," "Semiconductor Production," "Sensor," "Supply Chain," and "Sustainability," among others. The lobe structure facilitates the understanding and representation of supply chain elements. These lobes serve as taxonomies for classes and property clusters, bridging connections with other project components like the Arrowhead Cloud and enabling the realization of use cases.
-
Furthermore, when considering its practical implementation, we can turn our attention to the Applications in the SC4EU Project. Within the semiconductor domain, the SC4EU project harnesses the potential of Digital Reference. By addressing the bullwhip effect through data-driven strategies, SC4EU aims to alleviate industry challenges. Employing anonymous surveys and Multi-Party Computation technology, it effectively gathers reliable demand data. This information is then mapped onto semantic representations within the model and further processed with AI tools to achieve detailed demand breakdowns. Collaborating with advanced technologies like AI and the Semantic Web, the Digital Reference becomes a catalyst for transforming the SC4EU project. This transformation elevates the platform, enhancing demand forecasting accuracy and reducing chip shortages. Beyond immediate gains, this collaboration aligns with broader objectives, such as strengthening European digital sovereignty. The integration of cybersecurity, quality assurance, and reliability principles harmonizes with Industry 4.0 goals and the ongoing journey of digital transformation.
Lobes of Digital Reference